Addiction isn’t just about substances; it’s a gripping force that extends to certain behaviors. What makes these behaviors addictive is a loss of control and a persistent compulsion, even when faced with the fallout. Take gambling or excessive internet use, for instance — the patterns are familiar. There’s an undeniable urge, a drive that defies common sense, leading to a relentless pursuit regardless of the toll it takes on one’s life. Tolerance, withdrawal symptoms, and an escalating intensity further characterize these behaviors as addictive. This is known as a process addiction. Read on to find out more about this type of addiction.
If you or someone you know is grappling with addiction and seeking a path to recovery, don’t face it alone. Contact We Level Up CA today for your free and confidential call. Our compassionate team is here to support you on your journey to a healthier, addiction-free life. Take the first step towards recovery – contact us now. Your brighter future awaits.
What Is Process Addiction?
Process addiction, also known as behavioral addiction, is a pattern of compulsive engagement in certain behaviors or activities despite the negative consequences they may bring; unlike substance addictions involving drugs or alcohol, process addictions center around non-substance-related behaviors. These behaviors become problematic when individuals cannot control or stop them, disrupting their daily lives, relationships, and overall well-being.
Process addictions often share standard features with substance addictions, such as the development of tolerance, withdrawal symptoms, and interference with daily responsibilities. Examples of process addictions include gambling, internet use, work, and exercise, among others.
These addictive behaviors can have significant impacts on mental health, social functioning, and the ability to lead a balanced and fulfilling life. Treatment for process addiction often involves a combination of therapeutic interventions, support groups, and behavioral strategies to help individuals regain control over their compulsive behaviors and address the underlying issues contributing to their addiction.
When Is A Behavior Considered An Addiction?
A behavior is considered an addiction when it meets specific criteria that indicate a pattern of compulsive engagement despite adverse consequences. The term “addiction” is commonly associated with substance use disorders, but it can also apply to behaviors. The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5), which is a widely used diagnostic manual in the field of mental health, provides criteria for substance use disorders. Still, it does not precisely list criteria for behavioral or process addictions. However, some general indicators can help determine when a behavior may be considered addictive:
- Loss of Control: Individuals with addiction often find it challenging to control or stop the behavior, even when they want to.
- Compulsion: A strong, compelling urge to engage in the behavior exists.
- Continued Use Despite Consequences: The behavior persists despite negative consequences in various areas of life, such as health, relationships, work, or finances.
- Tolerance: Over time, there may be a need for more of the behavior to achieve the same level of satisfaction or pleasure.
- Withdrawal: The experience of negative emotional or physical symptoms when the behavior is reduced or stopped.
- Interference with Daily Life: The behavior interferes significantly with daily responsibilities, obligations, or social activities.
- Preoccupation: A significant amount of time is spent thinking about, planning, or engaging in the behavior.
- Escalation: Over time, there may be an escalation in the intensity or frequency of the behavior.
Professionals may use different criteria or models for different types of addictions. A comprehensive assessment by a qualified healthcare professional is typically necessary to determine whether a particular behavior meets the criteria for addiction and requires intervention or treatment.
Types Of Process Addiction
Process addictions encompass a range of compulsive behaviors that individuals engage in despite adverse consequences. Here are some common types of process addictions:
- Gambling Addiction: Involves a compulsive need to gamble, leading to negative consequences in various aspects of life, including finances and relationships.
- Internet and Technology Addiction: Excessive use of the internet, social media, online gaming, or other digital technologies, often leading to adverse effects on mental health and daily functioning.
- Work Addiction: Characterized by an obsessive focus on work to the detriment of personal relationships, physical health, and overall well-being.
- Shopping Addiction: Involves compulsive and excessive shopping, often leading to financial difficulties and emotional distress.
- Exercise Addiction: A preoccupation with exercise that goes beyond a healthy level, potentially leading to physical harm and neglect of other life responsibilities.
- Sexual Addiction: Compulsive engagement in sexual behaviors to the extent that it interferes with normal daily functioning and relationships.
- Eating Disorders: While not always classified as process addictions, disorders like binge eating or compulsive overeating share similarities with behavioral addictions.
- Gaming Addiction: Excessive and compulsive playing of video games leads to negative impacts on physical health, relationships, and daily activities.
- Love and Relationship Addiction: Involves a compulsive focus on romantic relationships, often seeking validation and identity through these connections.
The concept of process addiction is still evolving, and not all behaviors classified as such have reached consensus within the medical and psychological communities. Treatment for process addictions often involves a combination of therapeutic approaches, support groups, and behavioral interventions to address the underlying issues contributing to the addictive behaviors.
Skip To:
Learn More:
- Help for family members of drug addicts, Identifying Addiction, Helping vs Enabling, Interventions & Treatment
- How do Rehabilitation Centers Help? Recovery Time, Programs, Withdrawal Symptoms & The Principles of Effective Treatment at a Rehabilitation Center
- How to Help a Recovering Addict? Different actions you can take to help a loved one who’s suffering from addiction
- Best 101 Alcohol & Drug Addiction Quotes of All Time. Level Up with Recovery Quotes to Lift Your Spirit Anyday.
- 101 drug addiction quotes to help you on the way to recovery
- What Is Sobriety? Motivation, Recovery, Rehab, Personal Integrity, Vulnerability & Inpatient Rehab Treatment

Get Your Life Back
Find Hope & Recovery. Get Safe Comfortable Detox, Addiction Rehab & Dual Diagnosis High-Quality Care.
Hotline (855) 695-1160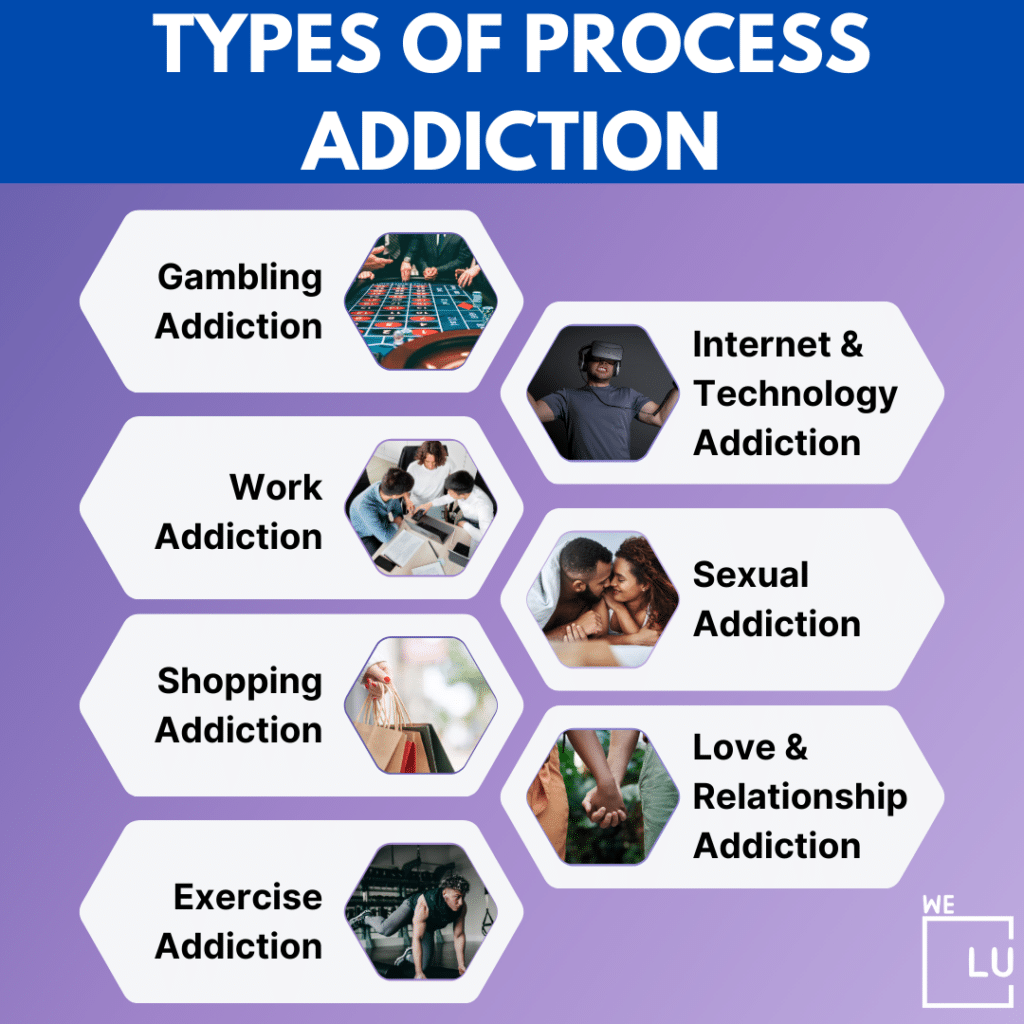
Why Are Certain Behaviors Considered Addiction?
Certain behaviors are considered addiction when they exhibit a pattern of compulsive engagement that persists despite adverse consequences. Addiction involves a loss of control over the behavior, with individuals finding it challenging to regulate or stop despite their desire to do so.
A key characteristic is the presence of a compelling urge, or compulsion, to engage in the behavior. Continued participation in the behavior despite adverse outcomes, such as negative effects on health, relationships, work, or finances, is a crucial indicator.
Additionally, the development of tolerance, where increasing amounts or intensity of the behavior are needed for the same level of satisfaction. Individuals may even experience withdrawal symptoms upon reducing or completely stopping to engage in the behavior. When behavior interferes significantly with daily life, preoccupies a substantial amount of time, and shows escalation over time, it is often identified as an addiction.
Get Help. Get Better. Get Your Life Back.
Searching for an Accredited Drug and Alcohol Rehab Centers in Near You?
Even if you have failed previously and relapsed, or are in the middle of a difficult crisis, we stand ready to support you. Our trusted behavioral health specialists will not give up on you. When you feel ready or just want someone to speak to about therapy alternatives to change your life call us. Even if we cannot assist you, we will lead you to wherever you can get support. There is no obligation. Call our hotline today.
FREE Addiction Hotline – Call 24/7How To Treat Process Addiction
Treatment for process addiction typically involves a combination of therapeutic interventions, support groups, and behavioral strategies to help individuals regain control over their compulsive behaviors and address underlying issues contributing to the addiction. A lot of these treatments overlap with treatments for substance abuse.
- Counseling and Psychotherapy: Individual or group therapy sessions with trained counselors or therapists can help individuals explore the root causes of their addictive behaviors, develop coping strategies, and gain insights into healthier ways of thinking and behaving.
- Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT is a widely used therapeutic approach that identifies and changes unhealthy thought patterns and behaviors. It can be effective in helping individuals manage triggers and develop coping skills.
- Motivational Enhancement Therapy (MET): MET is a therapeutic approach to enhance an individual’s motivation to change. It involves exploring and resolving ambivalence about the need for change and setting achievable goals.
- Support Groups: Joining support groups, such as 12-step programs like Gamblers Anonymous or Overeaters Anonymous, can provide individuals with a sense of community, understanding, and shared experiences. These groups often follow a structured program and offer ongoing support.
- Family Therapy: Involving family members in the treatment process can be crucial, as it helps address family dynamics, improve communication, and create a supportive environment for recovery.
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Practices promoting mindfulness and meditation can help individuals become more aware of their thoughts and behaviors, manage stress, and cultivate greater self-control.
- Medication: While medication is not typically the primary treatment for process addiction, certain medications may be prescribed to address co-occurring mental health issues, such as depression or anxiety, that contribute to addictive behaviors.
- Inpatient or Residential Treatment: For severe cases of process addiction, inpatient or residential treatment programs may be recommended. These programs provide a structured and supportive environment, often with 24-hour care, to help individuals break the cycle of addiction.
- Holistic Approaches: Some individuals benefit from holistic approaches such as yoga, art therapy, or acupuncture as complementary to traditional therapeutic methods.

Individuals with process addictions to seek professional help tailored to their specific needs. A comprehensive assessment by healthcare professionals can guide the development of an effective treatment plan. The level of care needed varies, and treatment plans are often personalized based on the individual’s unique circumstances and the specific nature of their addiction.
First-class Facilities & Amenities
World-class High-Quality Addiction & Mental Health Rehabilitation Treatment
Rehab Centers TourRenowned California Addiction Center. Serene Private Facilities. Inpatient rehab programs vary.
Addiction Helpline (855) 695-1160Proven recovery success experience, backed by a Team w/ History of:
15+
Years of Unified Experience
100s
5-Star Reviews Across Our Centers
10K
Recovery Success Stories Across Our Network
- Low Patient to Therapist Ratio
- Onsite Medical Detox Center
- Comprehensive Dual-Diagnosis Treatment
- Complimentary Family & Alumni Programs
- Coaching, Recovery & Personal Development Events

Can Process Addiction And Substance Addiction Happen At The Same Time?
Individuals can experience both substance addiction and behavioral addiction simultaneously. This co-occurrence is often referred to as comorbidity. In such cases, an individual may struggle with dependencies on substances such as drugs or alcohol while also exhibiting compulsive behaviors associated with process or behavioral addictions.
For example, someone with a substance use disorder may also engage in behaviors like compulsive gambling, excessive internet use, or problematic eating patterns. The coexistence of these conditions can complicate their situation, making treatment more complex.
Comprehensive treatment plans for individuals with both substance and behavioral addictions often involve addressing each aspect separately. This may include:
- Substance Abuse Treatment: This can involve detoxification, rehabilitation programs, counseling, and support groups specifically designed for substance use disorders.
- Behavioral Addiction Treatment: Therapeutic interventions, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), support groups, and counseling, may be employed to address the behavioral addiction aspect.
- Integrated Treatment: Some treatment programs integrate approaches that simultaneously address both substance and behavioral addictions. Integrated treatment recognizes the interconnectedness of these issues and aims to provide comprehensive care.
- Support Groups: Participating in support groups that focus on both substance and behavioral addictions can be beneficial, providing individuals with a supportive community that understands the complexities of dual addictions.
Individuals with co-occurring substance and behavioral addictions to seek professional help. Mental health professionals, addiction specialists, and treatment centers can tailor interventions to address the specific challenges associated with dual diagnoses and guide individuals on the path to recovery.
World-class, Accredited, 5-Star Reviewed, Effective Addiction & Mental Health Programs. Complete Behavioral Health Inpatient Rehab, Detox plus Co-occuring Disorders Therapy.
CALL (855) 695-1160End the Addiction Pain. End the Emotional Rollercoaster. Get Your Life Back. Start Drug, Alcohol & Dual Diagnosis Mental Health Treatment Now. Get Free No-obligation Guidance by Substance Abuse Specialists Who Understand Addiction & Mental Health Recovery & Know How to Help.
What Are The Underlying Causes Of Addiction?
The causes of addiction are complex and multifaceted, involving a combination of genetic, biological, environmental, and psychological factors. Addiction is a result of a combination of these elements, and individuals may have different risk factors that contribute to their vulnerability. Some key factors include:
- Genetic Factors: Genetics play a significant role in addiction susceptibility. Individuals with a family history of addiction may be more predisposed to developing addictive behaviors. Genetic variations can influence how the brain responds to substances or specific activities.
- Biological Factors: Changes in brain structure and function can contribute to addiction. Neurotransmitters such as dopamine, which play a role in pleasure and reward, may be affected, leading to the reinforcing nature of addictive substances or behaviors.
- Environmental Factors: Environmental influences, including early exposure to substances, trauma, stress, and a lack of family support, can contribute to the development of addiction. Adverse childhood experiences (ACEs) may increase the risk of substance abuse and behavioral addictions.
- Psychological Factors: Underlying mental health conditions, such as depression, anxiety, trauma, or other mood disorders, can contribute to the vulnerability to addiction. Individuals may use substances or engage in certain behaviors as a way of coping with emotional pain or distress.
- Social and Peer Influences: Social and peer pressures, especially during adolescence and young adulthood, can contribute to the initiation of substance use or engagement in addictive behaviors. The desire for acceptance and fitting in with peer groups can be powerful motivators.
- Developmental Factors: The stage of development can influence vulnerability to addiction. Adolescents and young adults, in particular, may be more susceptible due to ongoing brain development and the increased likelihood of engaging in risk-taking behaviors.
- Access to Substances or Behaviors: Easy access to substances or engaging stimuli, such as the availability of drugs, alcohol, or the prevalence of certain behaviors in the environment, can increase the risk of addiction.
- Personality Traits: Certain personality traits, such as impulsivity, sensation-seeking, and a lack of self-control, can contribute to the development of addictive behaviors.
Experience Transformative Recovery at the We Level Up California Treatment Center.
See our authentic success stories. Get inspired. Get the help you deserve.



Start a New Life
Begin with a free call to an addiction & behavioral health treatment advisor. Learn more about our dual-diagnosis programs. The We Level Up treatment center network delivers recovery programs that vary by each treatment facility. Call to learn more.
- Personalized Care
- Caring Accountable Staff
- World-class Amenities
- Licensed & Accredited
- Renowned w/ 100s 5-Star Reviews
We’ll Call You
Powerful Addiction Quotes & Inspirational Quotes Addiction Recovery & Quotes for Recovery Addicts.
Search We Level Up CA Process Addiction, Drug & Alcohol Rehab / Detox & Mental Health Topics & Resources
Sources
- Alavi SS, Ferdosi M, Jannatifard F, Eslami M, Alaghemandan H, Setare M. Behavioral Addiction versus Substance Addiction: Correspondence of Psychiatric and Psychological Views. Int J Prev Med. 2012 Apr;3(4):290-4. PMID: 22624087; PMCID: PMC3354400. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3354400/
- Grant JE, Potenza MN, Weinstein A, Gorelick DA. Introduction to behavioral addictions. Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse. 2010 Sep;36(5):233-41. doi: 10.3109/00952990.2010.491884. PMID: 20560821; PMCID: PMC3164585. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3164585/
- Chamberlain SR, Lochner C, Stein DJ, Goudriaan AE, van Holst RJ, Zohar J, Grant JE. Behavioural addiction-A rising tide? Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016 May;26(5):841-55. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2015.08.013. Epub 2015 Aug 24. PMID: 26585600.https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26585600/
- Figee M, Pattij T, Willuhn I, Luigjes J, van den Brink W, Goudriaan A, Potenza MN, Robbins TW, Denys D. Compulsivity in obsessive-compulsive disorder and addictions. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016 May;26(5):856-68. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2015.12.003. Epub 2015 Dec 11. PMID: 26774279. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26774279/
- Grant JE, Chamberlain SR. Impulsive action and impulsive choice across substance and behavioral addictions: cause or consequence? Addict Behav. 2014 Nov;39(11):1632-1639. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2014.04.022. Epub 2014 May 10. PMID: 24864028. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24864028/
- Kotyuk E, Magi A, Eisinger A, Király O, Vereczkei A, Barta C, Griffiths MD, Székely A, Kökönyei G, Farkas J, Kun B, Badgaiyan RD, Urbán R, Blum K, Demetrovics Z. Co-occurrences of substance use and other potentially addictive behaviors: Epidemiological results from the Psychological and Genetic Factors of the Addictive Behaviors (PGA) Study. J Behav Addict. 2020 Jun 26;9(2):272-288. doi: 10.1556/2006.2020.00033. PMID: 32609628; PMCID: PMC8939407. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32609628/
- Petry NM, Zajac K, Ginley MK. Behavioral Addictions as Mental Disorders: To Be or Not To Be? Annu Rev Clin Psychol. 2018 May 7;14:399-423. doi: 10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-032816-045120. PMID: 29734827; PMCID: PMC5992581. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29734827/
- Derevensky JL, Hayman V, Lynette Gilbeau. Behavioral Addictions: Excessive Gambling, Gaming, Internet, and Smartphone Use Among Children and Adolescents. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2019 Dec;66(6):1163-1182. doi: 10.1016/j.pcl.2019.08.008. PMID: 31679605. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31679605/
- Banz BC, Yip SW, Yau YH, Potenza MN. Behavioral addictions in addiction medicine: from mechanisms to practical considerations. Prog Brain Res. 2016;223:311-28. doi: 10.1016/bs.pbr.2015.08.003. Epub 2015 Nov 23. PMID: 26806783; PMCID: PMC6583773. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26806783/
- Potenza MN. Clinical neuropsychiatric considerations regarding nonsubstance or behavioral addictions. Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2017 Sep;19(3):281-291. doi: 10.31887/DCNS.2017.19.3/mpotenza. PMID: 29302225; PMCID: PMC5741111. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29302225/