Dilaudid Vs Oxycodone
What Is Dilaudid?
Dilaudid is the brand name for hydromorphone, which is a potent opioid analgesic (pain medication). It is a semi-synthetic derivative of morphine and is used to manage moderate to severe pain. Hydromorphone binds to specific receptors in the brain and spinal cord, known as opioid receptors, to reduce pain perception.
Dilaudid is available in various forms, including oral tablets, liquid solutions, and injectables. The injectable form is often used in hospitals for more rapid pain relief.
As an opioid, Dilaudid carries the risk of dependence, addiction, and other side effects. It is typically prescribed for short-term use, such as after surgery or for the management of severe pain due to conditions like cancer.
What Is Oxycodone?
Oxycodone is another opioid analgesic used for the relief of moderate to severe pain. Like hydromorphone (Dilaudid), oxycodone works by binding to opioid receptors in the brain and spinal cord, reducing the perception of pain. It is a semi-synthetic opioid derived from thebaine, a naturally occurring opiate alkaloid.
Oxycodone is available in various formulations, including immediate-release tablets, extended-release tablets, and in combination with other medications. The extended-release forms are designed to provide a prolonged release of the drug over an extended period, offering around-the-clock pain relief.
Common brand names for oxycodone include OxyContin (extended-release) and Percocet (combination with acetaminophen). It is often prescribed for conditions such as post-surgical pain, injury-related pain, and chronic pain associated with diseases like cancer.
Similar to other opioid medications, oxycodone has the potential for abuse, dependence, and addiction. It is crucial for individuals prescribed oxycodone to take it exactly as directed by their healthcare provider and to be aware of the potential risks and side effects.
Which Is Better For Pain?
The effectiveness of pain management depends on various factors, including the individual’s specific condition, the severity of the pain, and their medical history. Both Dilaudid (hydromorphone) and oxycodone are potent opioid analgesics commonly used for pain relief, but whether one is “better” than the other can vary from person to person.
Healthcare providers consider several factors when choosing a pain medication, including:
- Type and severity of pain: Different types of pain may respond differently to specific medications. Some individuals may find one medication more effective for their particular pain condition.
- Patient’s medical history: Existing health conditions, allergies, and other medications a person may be taking can influence the choice of pain medication.
- Individual response: People can respond differently to medications. What works well for one person may not be as effective for another, and individuals may also have different tolerances and sensitivities.
- Duration of pain relief needed: Some pain medications, such as extended-release formulations, provide longer-lasting relief, which can benefit chronic pain management.
- Risk factors: Opioid medications, including Dilaudid and oxycodone, carry risks of side effects, dependence, and addiction. Healthcare providers must consider these factors and assess the risk-to-benefit ratio for each individual.
Individuals with pain must work closely with their healthcare providers to find the most appropriate and effective pain management plan. Non-opioid options, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or alternative therapies, may also be considered depending on the nature of the pain.
Ultimately, there is no one-size-fits-all answer, and the choice between Dilaudid and oxycodone is based on careful consideration of the individual’s unique circumstances and needs. Always follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations and communicate openly about your response to the medication and any concerns or side effects you may experience.
Is Dilaudid Stronger Than Oxycodone?
Yes, hydromorphone (Dilaudid) is generally considered to be stronger than oxycodone. Hydromorphone is a more potent opioid compared to oxycodone, meaning that a smaller dose of hydromorphone is typically needed to achieve a similar level of pain relief as a larger dose of oxycodone.
The potency of opioid medications is often measured about morphine, and both hydromorphone and oxycodone are more potent than morphine. However, hydromorphone is considered to be among the most potent, commonly used opioid analgesics.
Dilaudid to Oxycodone Conversion
Converting from Dilaudid (hydromorphone) to oxycodone or any other opioid involves complex calculations and should be done by healthcare professionals. There is no simple, fixed conversion value that universally applies because individual responses to opioids can vary, and factors such as the specific formulations, dosages, and a patient’s opioid tolerance must be taken into account.
Healthcare providers use conversion tables, clinical experience, and their judgment to determine an appropriate conversion ratio based on each patient’s specific circumstances. Attempting to convert medications without professional guidance can lead to serious consequences, including inadequate pain control or an increased risk of side effects.

Skip To:
Learn More:
- Oxycodone Side Effects, Uses, Interactions, Addiction Facts
- How Long Does Oxycodone Take To Work? Timeline and Factors.
- Oxycodone Withdrawal Symptoms, Timeline, and Detox
- Does Oxycodone Make You Sleepy? Oxycodone Effects On Sleep
- How Long Does Oxycodone Stay In Your System?
- Oxycodone Vs Oxycontin. What Is The Difference And Similarities?
- Oxycodone and Hydrocodone, Side Effects, Forms, Dosages, Differences & Interactions
- Morphine Vs Oxycodone, Is Morphine Stronger Than Oxycodone?
- Dilaudid side effects, Less and Most Common Side Effects, Overdose, Addiction & Treatment
- Dilaudid Addiction, Specifics, Abuse, Signs of Addiction, Overdose & Treatment
- Dilaudid Detox, Addiction, Effects of Abuse, Withdrawal Symptoms, Duration, Timeline & Overdose Signs

Get Your Life Back
Find Hope & Recovery. Get Safe Comfortable Detox, Addiction Rehab & Dual Diagnosis High-Quality Care.
Hotline (855) 695-1160Dilaudid Uses
Dilaudid (hydromorphone) is an opioid analgesic primarily used for the management of moderate to severe pain. Here are some common medical uses for Dilaudid:
- Post-Surgical Pain: Dilaudid is often prescribed to manage pain after surgical procedures, providing relief during the initial recovery period.
- Severe Pain due to Injury: It may be used in acute and severe pain resulting from traumatic injuries, such as fractures or severe burns.
- Cancer Pain: Dilaudid can be used to alleviate pain associated with cancer, particularly in cases where other pain medications are insufficient.
- Pain Management in Palliative Care: In end-of-life care or palliative care settings, Dilaudid may help control severe pain and improve the quality of life for individuals with terminal illnesses.
- Pain in Chronic Conditions: In some instances, healthcare providers may prescribe Dilaudid to manage chronic pain conditions where other less potent analgesics have not provided sufficient relief.
The use of Dilaudid is generally reserved for situations where other pain management options have proven inadequate. The prescribing and monitoring of Dilaudid should be done under the close supervision of a healthcare professional due to the potential for side effects, dependence, and misuse associated with opioid medications. Patients should use Dilaudid exactly as their healthcare provider prescribes and promptly report any concerns or side effects.
Oxycodone Uses
Oxycodone is an opioid analgesic used primarily for the management of moderate to severe pain. Here are some common medical uses for oxycodone:
- Post-Surgical Pain: Oxycodone is often prescribed to manage pain after surgical procedures, providing relief during the recovery period.
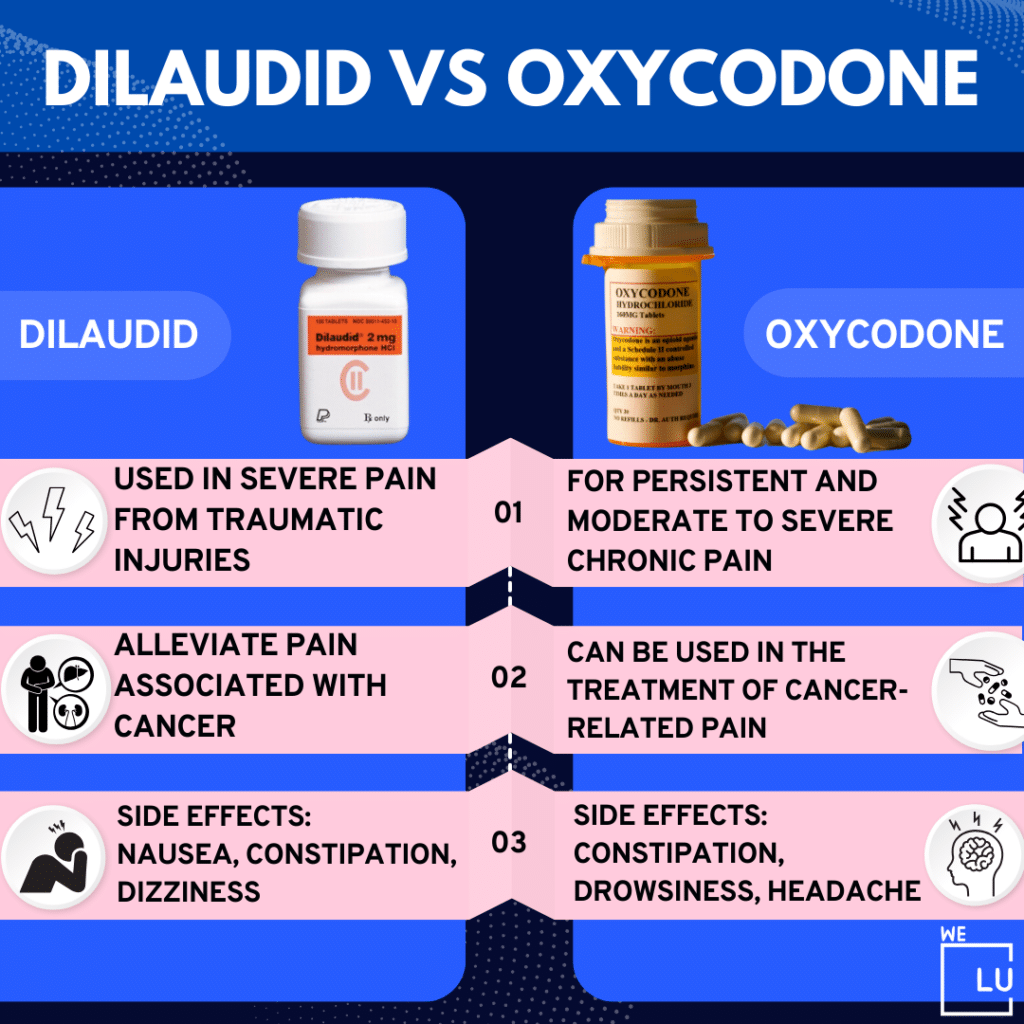
- Chronic Pain: In cases of persistent and moderate to severe chronic pain, such as pain associated with certain medical conditions or long-term injuries, oxycodone may improve the patient’s quality of life.
- Cancer Pain: Oxycodone can be employed in the treatment of cancer-related pain, especially when other pain management strategies are insufficient.
- Pain Management in Palliative Care: In end-of-life care or palliative care settings, oxycodone may be used to help control severe pain and enhance the comfort of individuals with terminal illnesses.
- Injury-Related Pain: Oxycodone may be prescribed for acute and severe pain resulting from injuries, such as fractures, severe burns, or other traumatic events.
- Extended-Release Formulations: Extended-release forms of oxycodone, such as OxyContin, are designed to provide around-the-clock pain relief and may be used for chronic conditions requiring continuous pain management.
Oxycodone is a potent opioid medication, and healthcare professionals should carefully manage its use. The potential for side effects, dependence, and misuse associated with opioids requires close monitoring and adherence to prescribed dosages. Patients should use oxycodone only as directed by their healthcare provider and communicate any concerns or side effects promptly.
When To Use Oxycodone Vs Dilaudid
The decision to use oxycodone or Dilaudid (hydromorphone) depends on several factors, and it is typically determined by a healthcare professional based on the individual patient’s needs, medical history, and the nature of the pain being treated. Both medications are potent opioids, and their use requires careful consideration.
Here are some general considerations for when oxycodone or Dilaudid might be chosen:
- Severity of Pain: Both oxycodone and Dilaudid are effective for managing moderate to severe pain. The choice may depend on the specific level of pain the patient is experiencing.
- Individual Response: Individual responses to opioids can vary. Some patients may respond better to one medication over the other, and the choice may be influenced by the patient’s previous experiences with pain management.
- Type of Pain: The type of pain being treated can influence the choice between oxycodone and Dilaudid. For example, Dilaudid is sometimes preferred in acute situations, such as post-surgical pain, while oxycodone may be used for chronic pain conditions.
- Formulation: Both medications are available in various formulations, including immediate-release and extended-release forms. The need for rapid pain relief or around-the-clock pain management may influence the choice.
- Health Status: The patient’s overall health, medical history, and any pre-existing conditions can influence the choice of opioids. Certain medical conditions may make one medication more suitable than the other.
- Prescribing Practices: Healthcare providers may have preferences based on their experiences and prescribing practices. They may choose one opioid over the other based on their familiarity with the medications.
- Patient Preferences: Patient preferences and considerations, such as convenience, side effect profiles, or concerns about specific formulations, may also play a role in the decision-making process.
Patients need to communicate openly with their healthcare providers about their pain levels, preferences, and any concerns or side effects experienced. Only a qualified healthcare professional can determine the most appropriate opioid medication and dosage for an individual patient’s needs.
Get Help. Get Better. Get Your Life Back.
Searching for an Accredited Drug and Alcohol Rehab Centers in Near You?
Even if you have failed previously and relapsed, or are in the middle of a difficult crisis, we stand ready to support you. Our trusted behavioral health specialists will not give up on you. When you feel ready or just want someone to speak to about therapy alternatives to change your life call us. Even if we cannot assist you, we will lead you to wherever you can get support. There is no obligation. Call our hotline today.
FREE Addiction Hotline – Call 24/7Dilaudid Side Effects
Common side effects of Dilaudid include:
- Respiratory Depression: Opioids like Dilaudid can slow down breathing, especially at higher doses. This is a serious side effect that requires immediate medical attention.
- Constipation: Opioids often cause constipation, and individuals taking Dilaudid may need to use stool softeners or laxatives under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Some people may experience nausea or vomiting, particularly when first starting the medication.
- Dizziness or Lightheadedness: Dilaudid can cause dizziness or lightheadedness, especially when standing up quickly. Patients should be cautious when changing positions.
- Sedation: Dilaudid can cause drowsiness or sedation, and individuals should avoid activities that require alertness, such as driving or operating heavy machinery until they know how the medication affects them.
- Itching or Rash: Some individuals may experience itching or develop a rash.
- Headache: Headache is a common side effect of Dilaudid.
- Sweating: Excessive sweating can occur as a side effect.
- Dry Mouth: Opioids can cause dry mouth.
- Urinary Retention: Difficulty urinating or a decrease in the frequency of urination can occur.
Oxycodone Side Effects
Common side effects of oxycodone include:
- Respiratory Depression: Opioids, including oxycodone, can suppress respiratory function, especially at higher doses. This is a severe side effect that requires immediate medical attention.
- Constipation: Opioids often cause constipation, and individuals taking oxycodone may need to use stool softeners or laxatives under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Some people may experience nausea or vomiting, particularly when first starting the medication.
- Dizziness or Lightheadedness: Oxycodone can cause dizziness or lightheadedness, especially when standing up quickly. Patients should be cautious when changing positions.
- Sedation: Oxycodone can cause drowsiness or sedation, and individuals should avoid activities that require alertness, such as driving or operating heavy machinery, until they know how the medication affects them.
- Itching or Rash: Some individuals may experience itching or develop a rash.
- Headache: Headache is a common side effect of oxycodone.
- Sweating: Excessive sweating can occur as a side effect.
- Dry Mouth: Opioids can cause dry mouth.
- Urinary Retention: Difficulty urinating or a decrease in the frequency of urination can occur.
Dilaudid Vs Oxycodone Warnings
Both Dilaudid (hydromorphone) and oxycodone are potent opioid medications, and their use comes with specific warnings and precautions. Here are some standard warnings associated with Dilaudid and oxycodone:
General Opioid Warnings
- Respiratory Depression: Opioids can cause respiratory depression, which is a slowing or stopping of breathing. This risk is higher at higher doses or in individuals with respiratory conditions. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience difficulty breathing.
- Risk of Dependence and Addiction: Both Dilaudid and oxycodone have the potential for physical dependence and addiction. These medications should be used only as prescribed by a healthcare professional, and patients should communicate openly about their pain levels and any concerns about dependence.
- Accidental Exposure: Keep these medications out of reach of children and others for whom they are not prescribed. Accidental exposure, especially in children, can be fatal.
- Interactions with Other Substances: Both Dilaudid and oxycodone can interact with other medications, substances, or alcohol. Inform your healthcare provider about all the medicines, supplements, and substances you use to avoid potential interactions.

Specific Dilaudid Warnings
- Risks of Intravenous Administration: The injectable form of Dilaudid is potent, and there are specific risks associated with intravenous administration, including the potential for serious or fatal respiratory depression.
Specific Oxycodone Warnings
- Acetaminophen Combination Warnings: Some formulations of oxycodone, such as Percocet, contain acetaminophen. Excessive use or overdose of acetaminophen can lead to severe liver damage.
- Extended-Release Formulation Precautions: Extended-release forms of oxycodone, like OxyContin, should not be crushed or chewed as this can lead to a rapid release of the medication, increasing the risk of overdose.
- Alcohol Warning: Both Dilaudid and oxycodone carry warnings about the potential for increased sedation and respiratory depression when used in combination with alcohol.
Make sure to discuss any medical conditions, medications, or concerns with your healthcare provider before starting or changing opioid therapy. These medications should be used cautiously and only as directed to minimize risks and maximize benefits. Consult your healthcare provider promptly if you have questions or experience adverse effects.
First-class Facilities & Amenities
World-class High-Quality Addiction & Mental Health Rehabilitation Treatment
Rehab Centers TourRenowned California Addiction Center. Serene Private Facilities. Inpatient rehab programs vary.
Addiction Helpline (855) 695-1160Proven recovery success experience, backed by a Team w/ History of:
15+
Years of Unified Experience
100s
5-Star Reviews Across Our Centers
10K
Recovery Success Stories Across Our Network
- Low Patient to Therapist Ratio
- Onsite Medical Detox Center
- Comprehensive Dual-Diagnosis Treatment
- Complimentary Family & Alumni Programs
- Coaching, Recovery & Personal Development Events

Dilaudid And Oxycodone Drug Interaction
Dilaudid (hydromorphone) and oxycodone are both opioids and combining them may increase the risk of specific side effects and complications. Any use of opioids, especially in combination, should be done under the supervision and guidance of a healthcare professional. Here are some considerations regarding potential drug interactions between Dilaudid and oxycodone:
- Central Nervous System Depression: Both Dilaudid and oxycodone can cause central nervous system depression, leading to drowsiness, dizziness, and impaired cognitive and motor function. Combining them may intensify these effects, making driving or operating heavy machinery unsafe.
- Respiratory Depression: Combining opioids increases the risk of respiratory depression, which is a slowing or stopping of breathing. This is a serious and potentially life-threatening side effect. The risk is higher when combining potent opioids like Dilaudid and oxycodone.
- Sedation: The sedative effects of both medications can be additive, increasing the likelihood of excessive sedation and impairment.
- Constipation: Opioids, including Dilaudid and oxycodone, commonly cause constipation. Combining them may increase the severity of this side effect.
- Interactions with Other Medications: Both Dilaudid and oxycodone can interact with other medications. To avoid potential interactions, you must inform your healthcare provider about all the medicines, supplements, and substances you are taking.
- Increased Risk of Dependence and Addiction: Using multiple opioids simultaneously may increase the risk of developing dependence and addiction.
- Liver Function: Some formulations of oxycodone, such as Percocet, contain acetaminophen, which can affect the liver. Combining medications with acetaminophen may increase the risk of liver-related complications.
Make sure to communicate openly with your healthcare provider about all the medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements. They can guide the appropriate use of these medications, adjust dosages if necessary, and monitor for potential interactions or complications.
Never combine or adjust the dosage of opioid medications without consulting your healthcare provider. If you experience adverse effects or have concerns about your medication regimen, seek prompt medical attention.
World-class, Accredited, 5-Star Reviewed, Effective Addiction & Mental Health Programs. Complete Behavioral Health Inpatient Rehab, Detox plus Co-occuring Disorders Therapy.
CALL (855) 695-1160End the Addiction Pain. End the Emotional Rollercoaster. Get Your Life Back. Start Drug, Alcohol & Dual Diagnosis Mental Health Treatment Now. Get Free No-obligation Guidance by Substance Abuse Specialists Who Understand Addiction & Mental Health Recovery & Know How to Help.
Dilaudid Vs Oxycodone Addiction
Opioid addiction is a serious medical condition characterized by a compulsive need for the drug, loss of control over its use, and continued use despite negative consequences.
Here are some key points regarding Dilaudid vs. oxycodone addiction:
- Similar Risk of Addiction:
- Both Dilaudid and oxycodone belong to the same class of drugs and have a similar potential for abuse, dependence, and addiction. They act on the same opioid receptors in the brain, leading to similar addictive properties.
- Risk Factors:
- Individual susceptibility to opioid addiction can vary, but certain factors may increase the risk. These include a personal or family history of substance abuse, mental health disorders, and genetic factors.
- Physical Dependence:
- Both medications can lead to physical dependence, where the body becomes accustomed to the presence of the drug. This can result in withdrawal symptoms when the drug is reduced or stopped.
- Tolerance:
- Tolerance can develop with both Dilaudid and oxycodone, requiring higher doses over time to achieve the same level of pain relief. Tolerance is also a risk factor for the development of addiction.
- Medical Supervision:
- Healthcare professionals should closely monitor the use of these medications. They are typically prescribed for short-term use or in specific medical situations, and the dosages should be carefully controlled.
- Proper Use and Follow-up:
- Individuals must use Dilaudid or oxycodone exactly as prescribed by their healthcare provider. Regular follow-up appointments allow for assessment of pain management, monitoring for side effects, and adjustments to the treatment plan if needed.
- Gradual Tapering:
- When discontinuing these medications, healthcare providers often recommend a gradual tapering of the dosage to minimize withdrawal symptoms and the risk of rebound pain.
- Alternative Pain Management Strategies:
- Healthcare providers may explore alternative pain management strategies or non-opioid medications for chronic pain to minimize the risk of long-term opioid use and potential addiction.
Individuals using these medications to be aware of the risks, communicate openly with their healthcare provider, and seek help if they have concerns about dependence or addiction. If you or someone you know is struggling with opioid addiction, seek professional assistance for comprehensive evaluation and treatment.
Experience Transformative Recovery at the We Level Up California Treatment Center.
See our authentic success stories. Get inspired. Get the help you deserve.



Start a New Life
Begin with a free call to an addiction & behavioral health treatment advisor. Learn more about our dual-diagnosis programs. The We Level Up treatment center network delivers recovery programs that vary by each treatment facility. Call to learn more.
- Personalized Care
- Caring Accountable Staff
- World-class Amenities
- Licensed & Accredited
- Renowned w/ 100s 5-Star Reviews
We’ll Call You
Joey’s Opiates Alcohol Drugs Addiction Recovery Story After Death of His Son at 26 From Fentanyl OD
Search We Level Up CA Dilaudid Vs Oxycodone Drug & Alcohol Rehab / Detox & Mental Health Topics & Resources
Sources
- WHO Guidelines for the Pharmacological and Radiotherapeutic Management of Cancer Pain in Adults and Adolescents. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2018. ANNEX 6, Pharmacological Profiles and Opioid Conversion Tables. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537482/ Read More: Dilaudid Vs Oxycodone, Oxycodone To Dilaudid, Is Oxycodone Stronger Than Dilaudid,
- Bhatnagar M, Pruskowski J. Opioid Equivalency. [Updated 2022 Sep 12]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK535402/ Read More: Dilaudid Vs Oxycodone, Oxycodone To Dilaudid, Is Oxycodone Stronger Than Dilaudid,
- US Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) – Use of Codeine, Oxycodone, and Other Opioids: Information for Employees – https://www.eeoc.gov/laws/guidance/use-codeine-oxycodone-and-other-opioids-information-employees Read More: Dilaudid Vs Oxycodone, Oxycodone To Dilaudid, Is Oxycodone Stronger Than Dilaudid,
- DEA – Oxycodone – https://www.dea.gov/factsheets/oxycodone
- MedLine Plus – Oxycodone – https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/meds/a682132.html
- FDA – Oxycontin Label – https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2008/020553s059lbl.pdf
- Sadiq NM, Dice TJ, Mead T. Oxycodone. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482226/
- Abi-Aad KR, Derian A. Hydromorphone. [Updated 2023 Aug 17]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470393/
- DEA – Hydromorphone Fact Sheet – https://www.dea.gov/factsheets/hydromorphone
- Cohen B, Ruth LJ, Preuss CV. Opioid Analgesics. [Updated 2023 Apr 29]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459161/ Read More: Dilaudid Vs Oxycodone, Oxycodone To Dilaudid, Is Oxycodone Stronger Than Dilaudid,
- Chou R, Hartung D, Turner J, et al. Opioid Treatments for Chronic Pain [Internet]. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2020 Apr. (Comparative Effectiveness Review, No. 229.) Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK556253/ Read More: Dilaudid Vs Oxycodone, Oxycodone To Dilaudid, Is Oxycodone Stronger Than Dilaudid,
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine; Health and Medicine Division; Board on Health Sciences Policy; Committee on Pain Management and Regulatory Strategies to Address Prescription Opioid Abuse; Phillips JK, Ford MA, Bonnie RJ, editors. Pain Management and the Opioid Epidemic: Balancing Societal and Individual Benefits and Risks of Prescription Opioid Use. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 2017 Jul 13. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK458660/ doi: 10.17226/24781 Read More: Dilaudid Vs Oxycodone, Oxycodone To Dilaudid, Is Oxycodone Stronger Than Dilaudid, Oxycodone Vs Dilaudid
- Zullo AR, Danko KJ, Moyo P, et al. Prevention, Diagnosis, and Management of Opioids, Opioid Misuse, and Opioid Use Disorder in Older Adults [Internet]. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2020 Nov. (Technical Brief, No. 37.) Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK564144/ Read More: Dilaudid Vs Oxycodone, Oxycodone To Dilaudid, Is Oxycodone Stronger Than Dilaudid, Oxycodone Vs Dilaudid